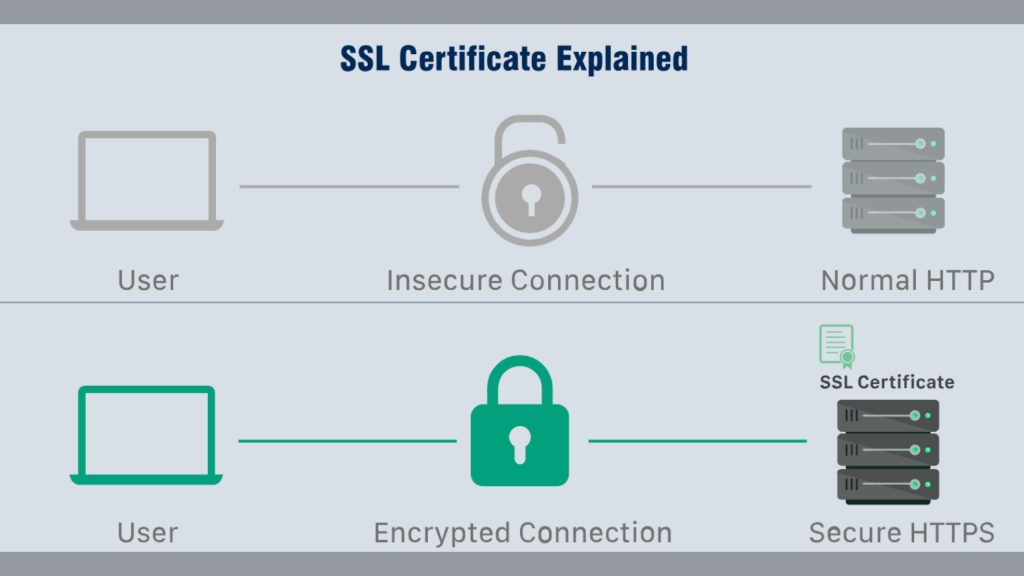
SSL certificate is a crucial security feature for websites that ensures safe and encrypted communication between a user’s browser and the web server. By using Secure Socket Layer (SSL) technology, these certificates protect sensitive data, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and personal information, from being intercepted by cybercriminals. When a website has an SSL certificate, the URL begins with “https,” indicating that the connection is secure. Enhances user trust but also helps in improving search engine rankings, making it an essential aspect for website owners to implement.
How do SSL Certificates Work?
SSL works by ensuring that any data transferred between users and websites, or between two systems, remains impossible to read. It uses encryption algorithms to scramble data in transit, which prevents hackers from reading it as it is sent over the connection. This data includes potentially sensitive information such as names, addresses, credit card numbers, or other financial details.
The process works like this:
- Browser or server attempts to connect to a website (i.e., a web server) secured with SSL.
- Browser or server requests that the web server identifies itself.
- Web server sends the browser or server a copy of its SSL certificate in response.
- Browser or server checks to see whether it trusts the SSL certificate. If it does, it signals this to the webserver.
- Web server then returns a digitally signed acknowledgment to start an SSL encrypted session.
- Encrypted data is shared between the browser or server and the webserver.
This process is sometimes referred to as an “SSL handshake.” While it sounds like a lengthy process, it takes place in milliseconds.
When a website is secured by an SSL certificate, the acronym HTTPS (which stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) appears in the URL. Without an SSL certificate, only the letters HTTP – i.e., without the S for Secure – will appear. A padlock icon will also display in the URL address bar. This signals trust and provides reassurance to those visiting the website.
To view an SSL certificate’s details, you can click on the padlock symbol located within the browser bar. Details typically included within SSL certificates include:
- The domain name that the certificate was issued for
- Which person, organization, or device it was issued to
- Which Certificate Authority issued it
- The Certificate Authority’s digital signature
- Associated subdomains
- Issue date of the certificate
- The expiry date of the certificate
- The public key (the private key is not revealed)
Why you need an SSL Certificate?
Websites need SSL certificates to keep user data secure, verify ownership of the website, prevent attackers from creating a fake version of the site, and convey trust to users.
If a website is asking users to sign in, enter personal details such as their credit card numbers, or view confidential information such as health benefits or financial information, then it is essential to keep the data confidential. SSL certificates help keep online interactions private and assure users that the website is authentic and safe to share private information with.
More relevant to businesses is the fact that an SSL certificate is required for an HTTPS web address. HTTPS is the secure form of HTTP, which means that HTTPS websites have their traffic encrypted by SSL. Most browsers tag HTTP sites – those without SSL certificates – as “not secure.” This sends a clear signal to users that the site may not be trustworthy – incentivizing businesses who have not done so to migrate to HTTPS.
SSL certificate helps to secure information such as:
- Login credentials
- Credit card transactions or bank account information
- Personally identifiable information — such as full name, address, date of birth, or telephone number
- Legal documents and contracts
- Medical records
- Proprietary information
Types of SSL Certificate
There are different types of SSL certificates with different validation levels. Six main types are:
- Extended Validation certificates (EV SSL)
- Organization Validated certificates (OV SSL)
- Domain Validated certificates (DV SSL)
- Wildcard SSL certificates
- Multi-Domain SSL certificates (MDC)
- Unified Communications Certificates (UCC)
Extended Validation Certificates (EV SSL)
This is the highest-ranking and most expensive type of SSL certificate. It tends to be used for high profile websites which collect data and involve online payments. When installed, this SSL certificate displays the padlock, HTTPS, name of the business, and the country on the browser address bar. Displaying the website owner’s information in the address bar helps distinguish the site from malicious sites. To set up an EV SSL certificate, the website owner must go through a standardized identity verification process to confirm they are authorized legally to the exclusive rights to the domain.
Organization Validated Certificates (OV SSL)
This version of SSL certificate has a similar assurance similar level to the EV SSL certificate since to obtain one; the website owner needs to complete a substantial validation process. This type of certificate also displays the website owner’s information in the address bar to distinguish from malicious sites. OV SSL certificates tend to be the second most expensive (after EV SSLs), and their primary purpose is to encrypt the user’s sensitive information during transactions. Commercial or public-facing websites must install an OV SSL certificate to ensure that any customer information shared remains confidential.
Domain Validated Certificates (DV SSL)
The validation process to obtain this SSL certificate type is minimal, and as a result, Domain Validation SSL certificates provide lower assurance and minimal encryption. They tend to be used for blogs or informational websites – i.e., which do not involve data collection or online payments. This SSL certificate type is one of the least expensive and quickest to obtain. The validation process only requires website owners to prove domain ownership by responding to an email or phone call. The browser address bar only displays HTTPS and a padlock with no business name displayed.
Wildcard SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL certificates allow you to secure a base domain and unlimited sub-domains on a single certificate. If you have multiple sub-domains to secure, then a Wildcard SSL certificate purchase is much less expensive than buying individual SSL certificates for each of them. Wildcard SSL certificates have an asterisk * as part of the common name, where the asterisk represents any valid sub-domains that have the same base domain. For example, a single Wildcard certificate for *website can be used to secure:
- payments.yourdomain.com
- login.yourdomain.com
- mail.yourdomain.com
- download.yourdomain.com
- anything.yourdomain.com
Multi-Domain SSL Certificate (MDC)
Multi-Domain certificate can be used to secure many domains and/or sub-domain names. This includes the combination of completely unique domains and sub-domains with different TLDs (Top-Level Domains) except for local/internal ones.
For example:
- www.example.com
- example.org
- mail.this-domain.net
- example.anything.com.au
- checkout.example.com
- secure.example.org
Multi-Domain certificates do not support sub-domains by default. If you need to secure both www.example.com and example.com with one Multi-Domain certificate, then both hostnames should be specified when obtaining the certificate.
Communications Certificate (UCC)
Communications Certificates (UCC) are also considered Multi-Domain SSL certificates. UCCs were initially designed to secure Microsoft Exchange and Live Communications servers. Today, any website owner can use these certificates to allow multiple domain names to be secured on a single certificate. UCC Certificates are organizationally validated and display a padlock on a browser. UCCs can be used as EV SSL certificates to give website visitors the highest assurance through the green address bar.
It is essential to be familiar with the different types of SSL certificates to obtain the right type of certificate for your website.
How to Obtain an SSL Certificate?
SSL certificates can be obtained directly from a Certificate Authority (CA). Certificate Authorities – sometimes also referred to as Certification Authorities – issue millions of SSL certificates each year. They play a critical role in how the internet operates and how transparent, trusted interactions can occur online.
The cost of an SSL certificate can range from free to hundreds of dollars, depending on the level of security you require. Once you decide on the type of certificate you require, you can then look for Certificate Issuers, which offer SSLs at the level you require.
Obtaining your SSL involves the following steps:
- Prepare by getting your server set up and ensuring your WHOIS record is updated and matches what you are submitting to the Certificate Authority (it needs to show the correct company name and address, etc.)
- Generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) on your server. This is an action your hosting company can assist with.
- Submitting this to the Certificate Authority to validate your domain and company details
- Installing the certificate they provide once the process is complete.
Once obtained, you need to configure the certificate on your web host or on your own servers if you host the website yourself.
How quickly you receive your certificate depends on what type of certificate you get and which certificate provider you procure it from. Each level of validation takes a different length of time to complete. Simple Domain Validation SSL certificate can be issued within minutes of being ordered, whereas Extended Validation can take as long as a full week.
Can an SSL Certificate be used on Multiple Servers?
It is possible to use one SSL certificate for multiple domains on the same server. Depending on the vendor, you can also use one SSL certificate on multiple servers. This is because of Multi-Domain SSL certificates, which we discussed above.
As the name implies, Multi-Domain SSL Certificates work with multiple domains. The number is left up to the specific issuing Certificate Authority. Multi-Domain SSL Certificate is different from a Single Domain SSL Certificate, which – again, as the name implies – is designed to secure a single domain.
To make matters confusing, you may hear Multi-Domain SSL Certificates, also referred to as SAN certificates. SAN stands for Subject Alternative Name. Every multi-domain certificate has additional fields (i.e., SANs), which you can use to list additional domains that you want to cover under one certificate.
Communications Certificates (UCCs) and Wildcard SSL Certificates also allow for multi-domains and, in the latter case, an unlimited number of subdomains.
What Happens When an SSL Certificate Expires?
When an SSL certificate expires, the secure connection between a user’s browser and the website is disrupted. This means the encrypted link that was protecting data transmission is no longer considered trustworthy. As a result, most modern web browsers will display a prominent warning message, such as “Your connection is not private” or “This site is not secure,” discouraging users from proceeding to the site.
Expired SSL certificate can have several negative consequences:
- Loss of Trust: Users are likely to abandon the site upon seeing a security warning, leading to a drop in traffic and reputation damage.
- Security Risks: Without a valid SSL certificate, data exchanged on the site is no longer encrypted, making it vulnerable to interception by hackers or malicious actors.
- SEO Impact: Search engines like Google favor secure websites. An expired certificate can negatively affect search rankings and visibility.
- Blocked Features: Certain browsers or applications may block access to the site entirely, especially on mobile devices or strict networks.
Renewing the SSL certificate before its expiration date is essential to maintaining continuous protection, user trust, and website performance.
How to Tell if a Site has an SSL Certificate?
The easiest way to see if a site has an SSL certificate is by looking at the address bar in your browser:
- If the URL begins with HTTPS instead of HTTP, that means the site is secured using an SSL certificate.
- Secure sites show a closed padlock emblem, which you can click on to see security details – the most trustworthy sites will have green padlocks or address bars.
- Browsers also show warning signs when a connection is not secure — such as a red padlock, a padlock which is not closed, a line going through the website’s address, or a warning triangle on top of the padlock emblem.
SSL certificate is a crucial digital security tool that encrypts data transferred between a user’s browser and a website. It helps protect sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal details from hackers. Beyond security, SSL certificates also build trust by displaying HTTPS and a padlock icon in the browser, signaling users that a website is safe and reliable. In today’s digital world, having an SSL certificate is not just a best practice – it’s a necessity for any website that values privacy, credibility, and user protection.
FAQs
What is an SSL certificate and why is it important?
SSL certificate is a digital certificate that encrypts data between a user’s browser and a website server. It ensures secure data transmission and builds trust by showing a padlock icon in the browser.
How does an SSL certificate work?
SSL works by establishing a secure encrypted connection between the browser and server using a public and private key. It ensures that any data transferred remains confidential and tamper-proof.
What are the different types of SSL certificates?
There are several types:
- Domain Validation (DV)
- Organization Validation (OV)
- Extended Validation (EV)
- Wildcard SSL
- Multi-Domain SSL (SAN SSL)
Each serves different security and business needs.
What are the benefits of using an SSL certificate?
SSL offers multiple benefits including:
- Data encryption
- User trust (padlock icon)
- Better SEO ranking
- Protection from phishing attacks
- Compliance with industry standards
Is SSL required for all websites?
Yes. Modern browsers label websites without SSL as “Not Secure,” especially those that collect user data, passwords, or payment details.
What’s the difference between HTTPS and SSL?
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) is the secure version of HTTP, and it uses SSL/TLS to encrypt the data between browser and server.
How can I tell if a website has an SSL certificate?
Look for “https://” in the website URL and a padlock icon in the address bar. Clicking the padlock shows certificate details.
How much does an SSL certificate cost?
SSL certificates can range from free (via Let’s Encrypt) to hundreds of dollars per year for EV SSLs with advanced validation and warranties.
How do I install an SSL certificate on my website?
Installation varies by hosting provider. Most platforms offer simple integration through cPanel or auto-install via services like Cloudflare or Let’s Encrypt.
Does SSL help with SEO rankings?
Yes, Google confirmed that websites with HTTPS (SSL) have a ranking advantage over those without encryption.